GBE > Encyclopaedia > Code > Jargon Buster > Entries > A > G#1335 N#1322
Acidification
Acidification
About:
Definition:
Acidification
Acidification is caused by acid depositions of three main pollutants: sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (Nox), and ammonia (NH3).
Acid depositions have negative impacts on water, forests, and soil as well as causing damage to buildings and monuments.
The main sources of emissions of acidifying substances are fossil fuel combustion used for energy production and transport.
(© DANTES ’06)
The result of acidifying pollutants emissions, such as SO2 or Nox, to the air.
These emissions have negative impacts on soil, groundwater, surface waters, biological organisms, ecosystems and materials.
(GreenSpec AEP ’09)
Acidification is caused by direct outlets of acids or by outlets of gases that form acid in contact with air humidity and are deposited to soil and water.
These acid depositions have negative impacts on natural ecosystems and the man‐made environment including buildings.1
(CAP’EM Compass PRé 2013)

Relevance to Sustainable Construction:
Durability:
- Even the most durable long life materials like copper and zinc claddings will suffer under the influence of acid rain.
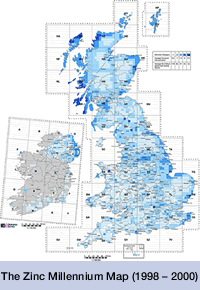
- Galvanizers Association Millennium Map shows the environmental pollution in the UK atmosphere from industry and how it effects the life expectancy if galvanized steel in that atmosphere.
Desulfurisation of flue gasses:
- To clean up the gases of power stations a chemical reaction is used, this generates a by-product: desulfurisation gypsum.
- This gypsum can be used in replacing virgin mined gypsum in construction boards used for internal linings:
- Plasterboards (Desulfurisation gypsum core and paper faced)
- Wood fibre reinforced gypsum dense boards (plantation thinings wood fibre, desulfurisation gypsum, recycled power station cooling water)
Opinion:
Examples:
Notes:
Construction Waste
BRE waste statistics indicate wastage factors of 30% from plasterboard linings, far higher than the 5-20% wastage factors allowed by Standard Methods of Measurement (SMM).
When gypsum or desulfurisation gypsum is mixed with biodegradable green waste in landfill, there is a high likelihood that the biodegradable waste will react with the gypsum and rerelease the chemicals filtered out on its creation, releasing the chemicals to atmosphere and potentially to create acid rain.
Gypsum is classified as stable non-active hazardous waste which must now be segregated and sent to special landfill site or special cells within landfills.
© GBE NGS ASWS BrianMurphy
aka BrianSpecMan
2006 – 18th February 2019
Acidification
Images:
© GBE NGS ASWS BrianMurphy
aka BrianSpecMan
18th December 2013 – 13th April 2015
Acidification
See also:
GBE Jargon Buster
- AP
- Acidification Potential (AP)
- Acid Rain
- Desulfurisation
- Desulfurisation Gypsum (DG)
- DG
- Gypsum
- Landfill
- LCA
- Life Cycle Assessment (LA)
- SNRHW
- Stable Non-Reactive Hazardous Waste (SNRHW)
GBE CPD
- Gypsum
- Violet materials
GBE Checklist
GBE Links
- Organisation/Website
GBE Calculator
GBE Projects
© GBE NGS ASWS BrianMurphy
aka BrianSpecMan
2012 – 18th December 2013