Form Factor Equation
GBE > Encyclopaedia > Files > Calculators > Equations > G#38342
Form Factor Equation
About:
Form Factor
- The ratio of external envelope area to floor area or volume ratios can be used as a design driver to improve building energy efficiency
- Simple singular cubical design is more efficient than multiple, long thin or sprawling buildings.
- Projections from the building envelop increase the form factor they include: Porches, conservatories, lean-to, bay windows, oriel windows, dormer roofs
- Projections do not include: roof overhand, balconies, walkways, access balconies, escape stairs
- Complexity of the external envelope will normally reflect badly in the energy efficiency stake due to the high risk of air leakiness and thermal bridging at corners and junctions and in the cost of its construction.
- Simplicity of the external envelop will normally lead to lower costs but there are always edges and corners in a rectilinear format.
- A spherical envelope is the most efficient means of enclosure (in terms of surface area to enclosed volume) and will lead to the simplest envelope without complications of edges and corners.
- The ability to make and purchase materials for spherical construction is limited, the costs will not be cheap and it is difficult to place a spherical building on the ground, better floating in air, space or under water or on the top of a supporting column.
- Once the form factor is established it should be used to modify the U value (UK) or R value (EU & Int)
- The higher the Form Factor the Lower the U value, the thicker the insulation, needs to be to make the building a low energy demand building.
- A correlation between Surface Area Form Factor and required thermal insulation thicknesses is a factor of 100:
- assuming a lambda k value of 0.044 w/m.K ≡ mineral fibre
- adjust for other material’s lambda k value
- adjust for other components in elements
- Form Factor SA/FA = 2: Insulation thickness = 200 mm
- Form Factor SA/FA = 3: Insulation thickness = 300 mm
- Form Factor SA/FA = 4: Insulation thickness = 400 mm
- etc.
- And don’t forget Decrement Delay
All of the above has been taken into accounts in the GBC Green Building Calculator V2.0.0.
- (due for release during August 2020)
Surface area to floor area ratio (SA/FA)
Equation:
Total Area of Thermal Envelop
Total Floor Area
Target ratio:
<3.0
Surface area to volume ratio (SA/V)
Equation:
Total Area of Thermal Envelop
Total internal Volume
Target ratio:
<0.7
GBE Social Media
GBE Q&A
Does the form matter for energy efficient homes?
ecokit.com.au
Yes!
My belief is that the form is an important part of dwellings for energy efficiency and even more so for energy self reliance to integrate solar PV, etc without disrupting the lines of the form.
© GBE GBC GBL NGS ASWS Brian Murphy aka BrianSpecMan **
6th April 2020 – 27th July 2020
Form Factor Equation
Images:

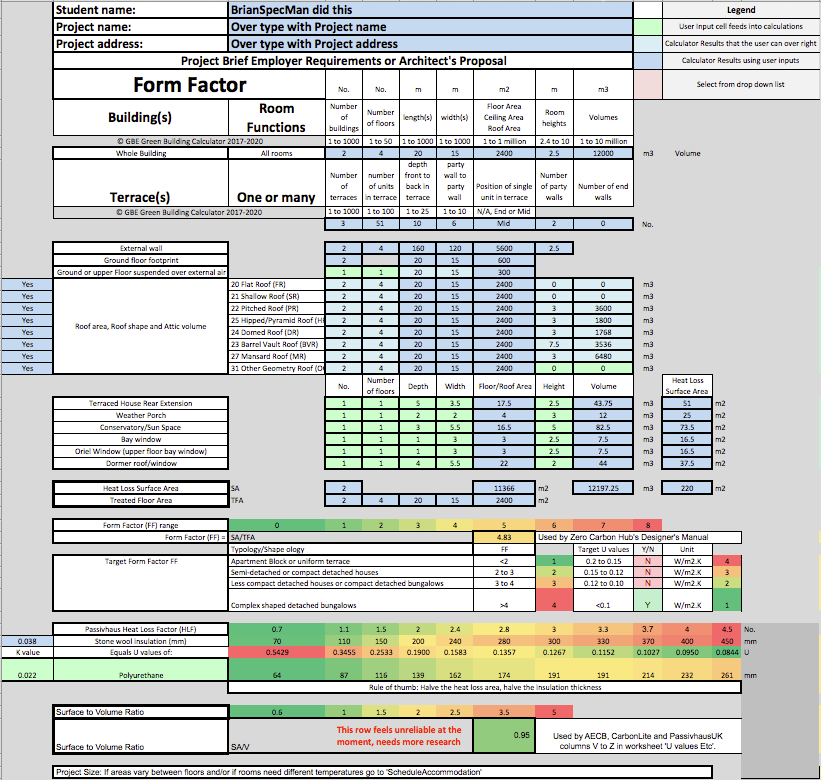
GBC Green Building Calculator FormFactor A15 BRM 270720 PNG
Above a snapshot of part of the sheet below
This may be extracted and made as a stand alone Excel file
It uses TBH The Building’s Hub publication The Designer’s Handbook page 8 data for the calculations.
I has also been developed for retrofit and new build forms and for add-ons including conservatory, porch, sun space, bay window, oriel window and dormer roofs, lean-to
Green Building Calculator V2.0.0. will include this update
Form Factor as shown here is one of the many worksheets
© GBE GBC GBL NGS ASWS Brian Murphy aka BrianSpecMan **
6th April 2020 – 27th July 2020
Form Factor Equation
See Also:
GBE Equations
- Form Factor (Equation) G#38342 (This page)
- Decrement Delay Factor (Equation) G#31148
GBE Lockdown Learning
- Lockdown Learning (Navigation) G#38210
- Building Form v Energy Efficiency
GBE Publications
- Zero Carbon Hub G#13351
- The Buildings Hub (TBH)
- TBH Designer’s Handbook PDF Page 8
GBE Datasets
- ICE Database (Jargon Buster) G#1018 N#1037
- Timber Species Schedule (Dataset) G#1371 N#1351
- Generic Materials Schedule (Dataset)
- Regulations/Design Guides Elemental U values/Airtightness (Dataset)
- Thermal Insulation Materials properties (Dataset)
GBE Calculators
- Whole Building Energy Demand
- Elemental % Comparison (Calculator)
- Fuel and In Use Carbon (Calculator)
- Regulations/Design Guides Elemental U values/Airtightness (Dataset)
- Form factor & U value (Calculator)
- Insulation v Glazing cost comparison (Calculator)
- Thermal Insulation Materials (Dataset)
- Insulation material > U value > Thickness (Calculator)
- Insulation material > Decrement Delay > Thickness (Calculator)
- Interstitial Condensation Check (Calculator)
- Whole Building U value, IUC, EE, EC, SC, LCA (Calculator)
- Whole Building EE EC SC (Calculator) G#1910 N#1764
- Whole Building U value (Calculator)
- WasteCost®lite (Calculator) G#531 N#551
- WasteCost®lite (Calculator) G#1297 N#1289
- Loft Insulation U value Raised deck support Psi value (Calculator) G#14582
- StoreFloor Thermal Bridge (Calculator) G#13287
- Scale Changer (Calculator) G#19287
GBE Calculators Other’s
- Carbon Calculator
- Decrement Calculators
- Embodied Carbon Database Launched 10/04/2014
- Psi value (Calculator Database)
- Shared Earth Building Embodied Carbon (Database) G#1307 N#1298
- Thermal Mass (Calculator) G#16163
- U Value Calculators
- U-value only Calculator App G#10630
GBE Calculators Shop
- Whole Building U value to In Use Carbon A05 XLSX (Shop) G#11009
- Whole Building U value to In Use Carbon A06 XLS (Shop) G#11095
- Whole Building EE EC SC A11 XLS (Shop) G#11090
- Whole Building EE EC SC A10 XLSX (Shop) G#10445
GBE Datasets Shop
- Timber Species Schedule (Shop) G#10656
By Others
- U-value Calculator App G#10630
- Shared Earth Building Embodied Carbon Database 12/02/13 G#1307 N#1298
GBE Jargon Buster
Initials, Abbreviations, Acronyms:
- AECB
- C
- CO2
- CO2e
- D&DT
- EC
- EE
- PHPP
- SAP
- SBEM
- SC
- TSB
- Building Embodied Carbon
- Building Embodied Energy
- Building Energy Demand
- Building Fuel demand and Carbon generated
- Building U Value
- CAPEM Compass
- Carbon lite
- Design & Decision Tools
- Decrement Delay Decrement Factor (Jargon Buster) G#14043
- Element area U Value
- Elemental section U Value
- Embodied Carbon (EC)
- Embodied Energy (EE)
- Embodied Water
- Equation
- Form Factor
- Fuel Carbon
- Innovate UK
- Lambda k value
- Passivhaus
- RetScreen
- Sequestered Carbon (SC)
- Shared Earth Building Embodied Carbon
- Technology Strategy Board (TSB)
- U value
- WasteCost®Lite (by GBE)
- Water Calculator (by AECB)
GBE Links
- AECB
- WRAP
- CarbonLite
- Innovate UK
- Passivhaus
- RetScreen
- Tandem Architecture Ecologique (Canada)
© GBE NGS ASWS Brian Murphy aka BrianSpecMan *
6th April 2020 – 25th April 2020


Form Factor is an essential part of the criteria. The worst the form factor the better the U value needs to be, to make an efficient low energy demand building. The more internal and external corners there are the higher the quantity of potential thermal bridges and air leakages; and the more expensive the building is too make.